Have you ever wondered why some girls have blonde hair while others have brown or red? It’s all thanks to a fascinating pigment called melanin, the secret ingredient that determines our unique hair color. But it’s not as simple as just one type of melanin – there’s actually a whole world of genetics at play!
The Melanin Magic: Eumelanin and Pheomelanin
Our hair follicles, tiny structures beneath our skin, contain cells called melanocytes. These melanocytes produce two main types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is responsible for shades of brown and black hair. The more eumelanin a person has, the darker their hair will be. Pheomelanin, on the other hand, creates red and yellow hues. Blondes have less eumelanin, while redheads produce primarily pheomelanin.
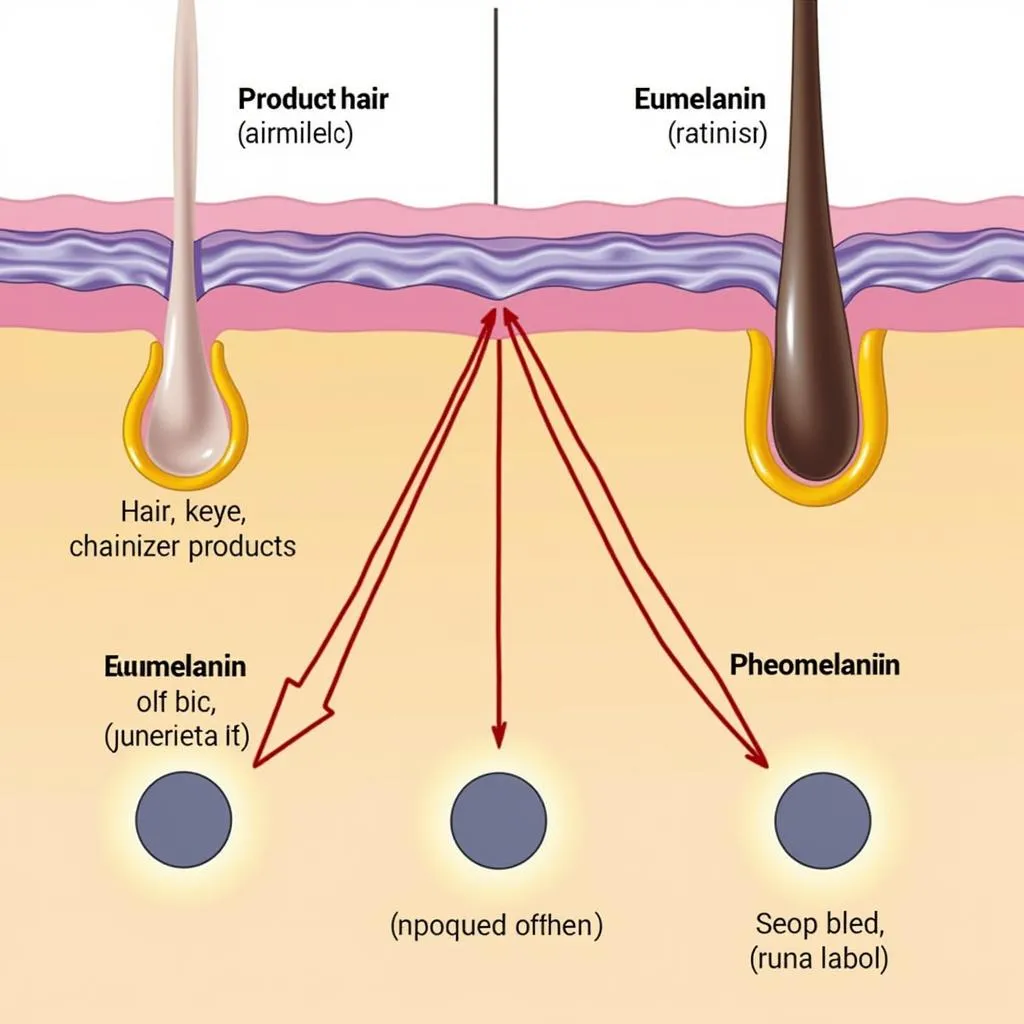 Melanin Production in Hair Follicles
Melanin Production in Hair Follicles
Genetics: The Blueprint of Our Hair Color
The exact combination of eumelanin and pheomelanin a person produces is determined by their genes, which they inherit from their parents. Each parent contributes one set of genes to their child, and these genes contain specific instructions for melanin production.
Think of it like this: if one parent has genes for high eumelanin production (dark hair) and the other parent has genes for low eumelanin production (light hair), their child might inherit a combination that results in medium-brown hair.
More Than Just Brown, Black, Blonde, and Red
Hair color isn’t always clear-cut. Some individuals may have a blend of eumelanin and pheomelanin, resulting in shades like auburn, strawberry blonde, or even dark brown with reddish undertones. The possibilities are truly diverse!
Can Hair Color Change Over Time?
Interestingly, a person’s hair color can change throughout their life. This is because the production of melanin can be influenced by factors like age, hormones, and even environmental factors.
For instance, many babies are born with lighter hair that gradually darkens as they grow older and produce more eumelanin. Additionally, hormonal changes during puberty or pregnancy can also affect melanin production, leading to subtle or sometimes more noticeable hair color shifts.
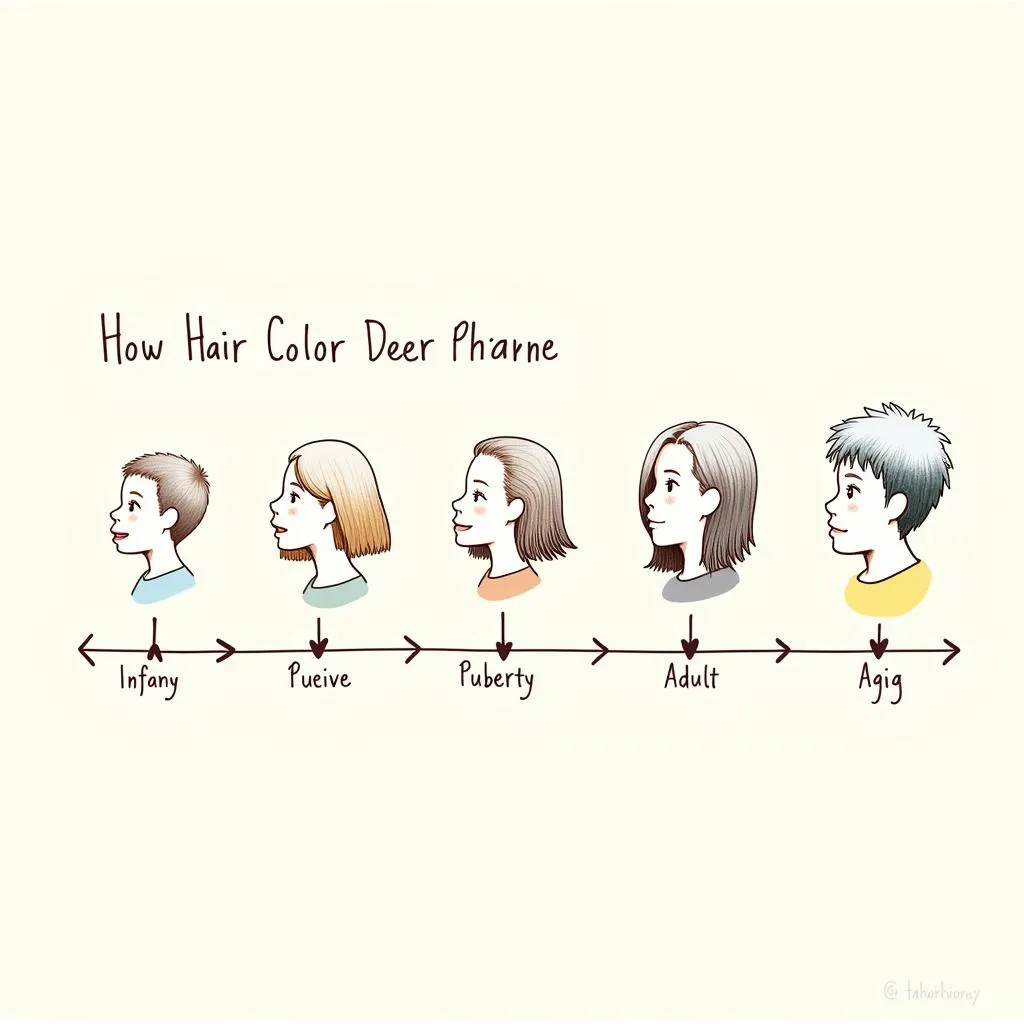 Timeline of Hair Color Change
Timeline of Hair Color Change
Beyond the Basics: Other Factors Influencing Hair Color
While genetics plays the most significant role, other factors can also subtly influence hair color:
- Sun Exposure: UV rays from the sun can lighten hair by breaking down melanin.
- Nutrition: A diet lacking in certain nutrients like copper or vitamin B12 may impact melanin production.
- Hair Products: Some hair dyes and styling products can temporarily alter hair color.
Conclusion
The diverse tapestry of human hair color is a fascinating interplay of genetics, melanin, and even external factors. Understanding the science behind what determines a girl’s hair color allows us to appreciate the uniqueness and beauty of every shade, from the deepest black to the lightest blonde and every hue in between.

