When you picture a wolf, what color comes to mind? Many people immediately think of a sleek, gray creature, and while this is certainly a common coat color for wolves, it’s far from the only one. The world of wolves is surprisingly diverse when it comes to their fur, with a fascinating range of hues and patterns found across different species and regions.
Beyond the Grayscale: Unpacking Wolf Coat Color Variations
While gray is a prevalent color in the wolf kingdom, nature has painted these majestic creatures with a much broader palette. Let’s delve into the spectrum of colors that grace wolf coats:
- Gray: The classic wolf color, often with subtle variations and blends of black, white, and brown. This coloration provides excellent camouflage in many environments, particularly in forests and rocky terrain.
- Black: Striking and powerful, black wolves are a sight to behold. This coloration is often linked to dominant genes and can be found in various wolf populations. Black wolves are particularly common in North America, where they blend seamlessly into dense forests.
- White: Pristine and ethereal, white wolves are often associated with Arctic regions, where their fur provides camouflage against the snowy backdrop. White wolves can also be found in other areas, with their coloration potentially influenced by genetic factors and environmental conditions.
- Brown: From rich chocolate to lighter tan shades, brown wolves showcase a warm and earthy palette. This coloration can be found in various wolf populations and is particularly well-suited for blending into forested and mountainous landscapes.
- Red: While not as common as other colors, red wolves, as their name suggests, exhibit a reddish or cinnamon hue. This unique coloration is found in a specific species of wolf native to the southeastern United States. Sadly, red wolves are critically endangered, making their distinctive coat color even rarer.
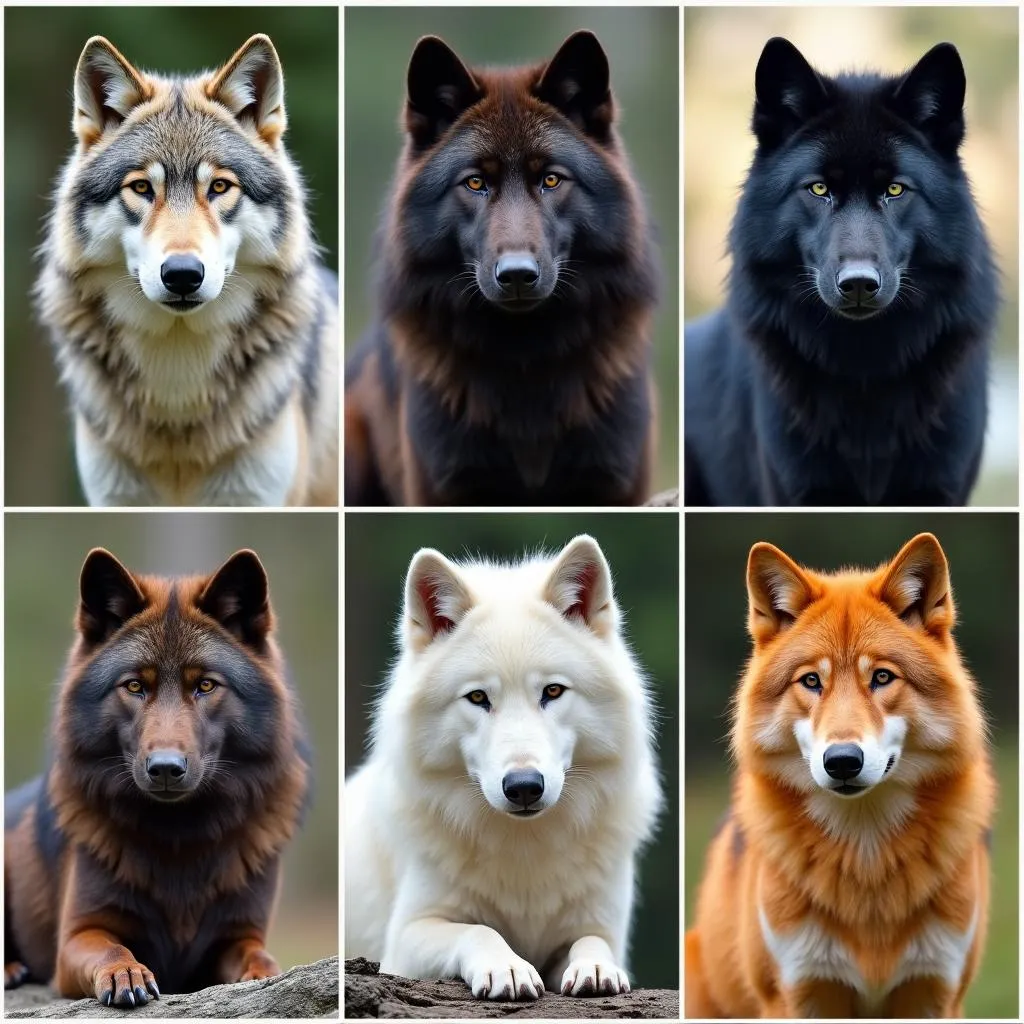 Wolves with different coat colors
Wolves with different coat colors
Factors Influencing Wolf Coat Color: Genetics and Environment
The wide array of wolf coat colors is a testament to the interplay of genetics and environment. Several factors contribute to the final hue and pattern of a wolf’s fur:
- Genetics: Like many physical traits, coat color in wolves is determined by genes inherited from their parents. Dominant and recessive genes interact to create the vast array of colors we see. For instance, the gene for black fur is often dominant over the gene for gray fur, explaining the prevalence of black wolves in some populations.
- Camouflage: The color of a wolf’s fur often serves as camouflage, helping it blend into its surroundings. Wolves living in snowy environments, like the Arctic wolf, tend to have white fur, while wolves in forested areas may have gray or brown fur that allows them to disappear into the shadows.
- Sun Exposure: The amount of sunlight a wolf receives can also influence its coat color. Wolves living in areas with intense sunlight may have lighter fur, while wolves in cloudier regions might have darker fur. This phenomenon is similar to how human skin can tan or lighten depending on sun exposure.
- Diet: While not as significant a factor as genetics or environment, a wolf’s diet may play a subtle role in coat color. Certain foods rich in pigments could potentially contribute to slight variations in fur hue.
The Significance of Coat Color: More Than Meets the Eye
A wolf’s coat color is not merely an aesthetic feature; it plays a crucial role in its survival and social dynamics:
- Camouflage and Hunting: As mentioned earlier, camouflage is essential for wolves, both as predators and potential prey. A coat that blends into the environment helps wolves ambush prey more effectively and avoid detection by larger predators.
- Social Signaling: Within a wolf pack, coat color can serve as a form of visual communication. Dominant wolves might have darker or more distinct markings, while subordinate wolves may exhibit lighter or less conspicuous coloration.
- Thermoregulation: The color of a wolf’s fur can also influence its body temperature. Darker fur absorbs more heat, which can be beneficial in colder climates. Lighter fur, on the other hand, reflects sunlight and helps wolves stay cool in warmer regions.
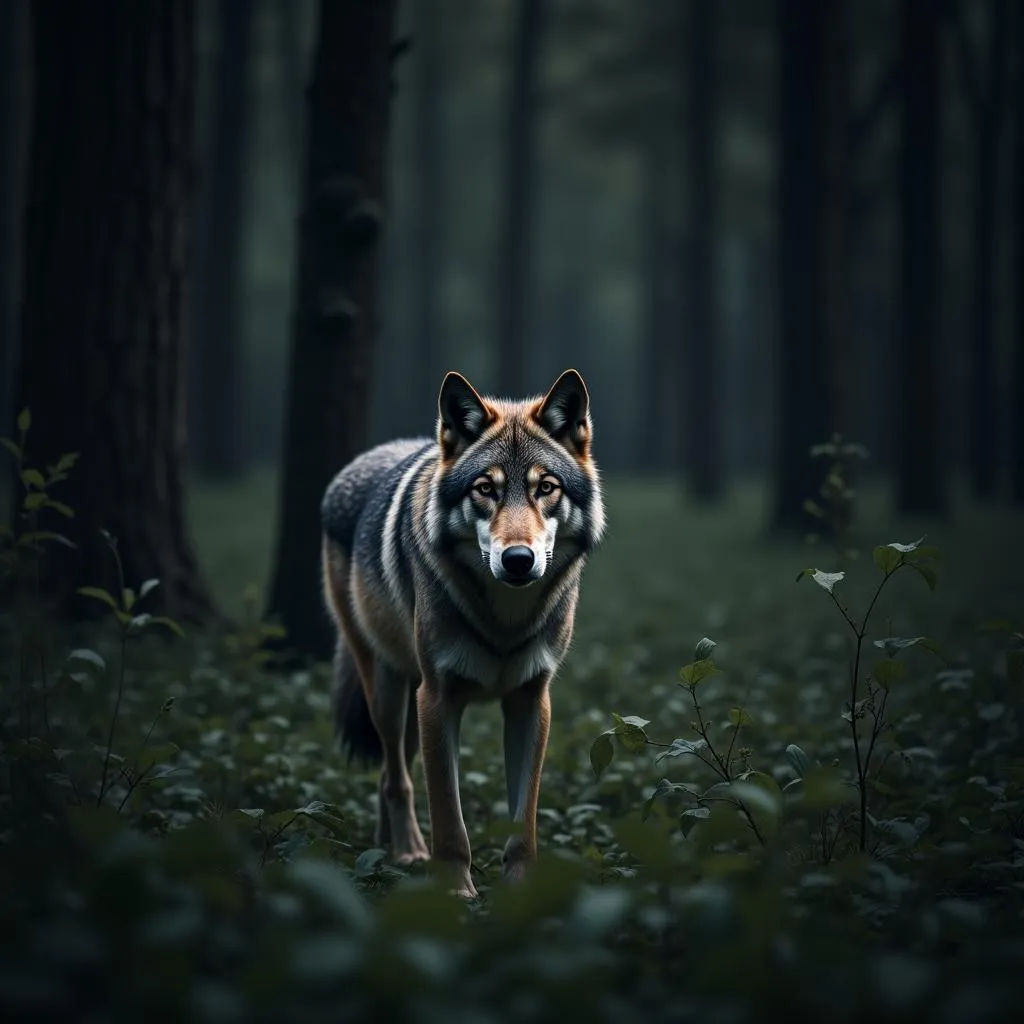 A gray wolf camouflaged in a forest
A gray wolf camouflaged in a forest
Beyond Color: The Intricate Patterns of Wolf Coats
The diversity of wolf coats extends beyond color to encompass a range of patterns and markings. These patterns, often subtle and intricate, can further enhance a wolf’s camouflage and visual communication.
- Agouti: The agouti pattern, characterized by individual hairs with bands of different colors, is common in many wolf populations. This pattern creates a grizzled or blended appearance, providing excellent camouflage in a variety of environments.
- Countershading: Some wolves exhibit countershading, with darker fur on their backs and lighter fur on their undersides. This pattern helps break up the animal’s outline, making it more difficult to spot against varied backgrounds.
- Facial Masks: Many wolves have distinctive facial masks, with markings around their eyes, muzzles, and ears. These markings can vary greatly in shape, size, and color and may play a role in individual recognition within a pack.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Spectrum of Wolf Beauty
From the classic gray to the striking black and the pristine white, the world of wolf coats is a testament to the power of nature’s artistry. Understanding the factors that influence coat color and the roles it plays in a wolf’s life deepens our appreciation for these magnificent creatures. The next time you envision a wolf, remember that its coat color is more than just a hue; it’s a reflection of its genetics, environment, and place in the intricate tapestry of the wild.
FAQs:
1. What is the rarest wolf color?
While all wolf colors are beautiful, the rarest is arguably red. Red wolves, with their distinctive reddish or cinnamon hue, are a critically endangered species native to the southeastern United States.
2. Are all white wolves albinos?
Not necessarily. While some white wolves may be albino, lacking pigment in their fur and skin, others simply inherit genes for white fur.
3. Can wolves change their coat color?
Wolves typically don’t change their base coat color. However, they do undergo seasonal molts, shedding their winter coats for lighter summer coats. This can make their fur appear slightly different depending on the time of year.
4. Do wolf pups have the same coat color as their parents?
Not always. Wolf pups inherit genes from both parents, and the combination of these genes determines their coat color. This means pups can have different coat colors than either parent, especially if recessive genes are involved.
5. Is there a link between a wolf’s coat color and its personality?
There’s no scientific evidence to suggest a direct link between a wolf’s coat color and its personality.
Need help choosing the perfect colors for your next project? Contact us at: 0373298888 or email us at: [email protected]. You can also visit our showroom at: 86 Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội. Our team is available 24/7 to assist you!
For more fascinating insights into the world of wolves, check out our article on are wolf dogs legal in colorado.