Shading with colors is a fundamental technique in art and design that adds depth, dimension, and realism to your work. By understanding how light interacts with objects and applying different shades of color, you can create stunning visual effects that bring your creations to life. Whether you’re a painter, illustrator, or simply someone who wants to enhance their understanding of color, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to master the art of shading with colors.
Understanding Color Theory for Shading
Before we dive into the practical techniques of shading, it’s crucial to grasp some basic color theory concepts.
- Hue: This refers to the pure form of a color, such as red, blue, or green.
- Saturation: Saturation describes the intensity or purity of a color. A highly saturated color appears vibrant, while a less saturated color looks duller.
- Value: Value represents the lightness or darkness of a color. It’s the most crucial element in shading, as it creates the illusion of depth and volume.
When shading, you’ll primarily be manipulating the value of colors to depict how light affects an object. Lighter values suggest areas where light hits directly, while darker values indicate shadows and areas further from the light source.
Choosing a Color Palette for Shading
Selecting the right color palette is crucial for effective shading. Here’s a breakdown of different approaches:
- Monochromatic Shading: This technique involves using different values of a single color to create shading. It’s a simple yet effective method for achieving a harmonious and unified look.
- Analogous Shading: Analogous colors are adjacent to each other on the color wheel. Using analogous colors for shading creates a sense of harmony and subtle variations in temperature.
- Complementary Shading: Complementary colors are opposite each other on the color wheel, such as red and green or blue and orange. Using complementary colors for shading can create vibrant contrasts and visually striking effects.
The choice of color palette depends on the desired mood, style, and subject matter. Experiment with different palettes to discover what works best for your artistic vision.
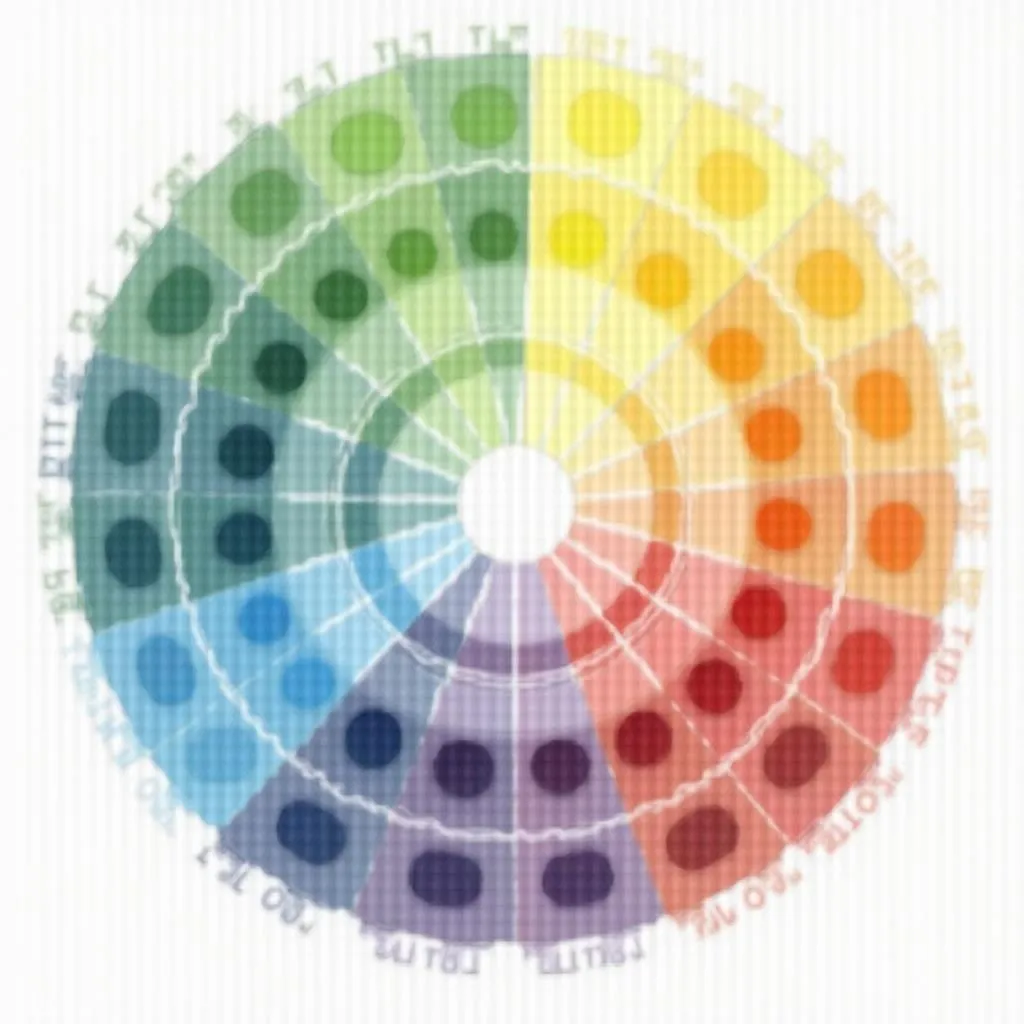 Color Wheel with Shading Types
Color Wheel with Shading Types
Techniques for Shading with Colors
Now that you understand the fundamentals, let’s explore some common techniques for shading with colors:
1. Blending
Blending is a fundamental technique that involves smoothly transitioning between different values of color. By gradually blending lighter and darker shades, you can create soft transitions that mimic the way light naturally falls on objects.
2. Hatching and Cross-Hatching
Hatching involves creating parallel lines to build up value. Cross-hatching takes this further by layering lines in different directions. These techniques are excellent for adding texture and dimension to your shading.
3. Stippling
Stippling utilizes small dots or marks to create value. By varying the density and size of the dots, you can achieve a wide range of values and textures. Stippling is particularly effective for creating subtle gradients and realistic textures.
4. Scumbling
Scumbling involves applying a thin, broken layer of color over another. This technique is useful for creating subtle variations in color and texture, adding depth and complexity to your shading.
5. Glazing
Glazing involves applying thin, transparent layers of color over a base layer. This technique allows you to gradually build up color intensity and create luminous effects.
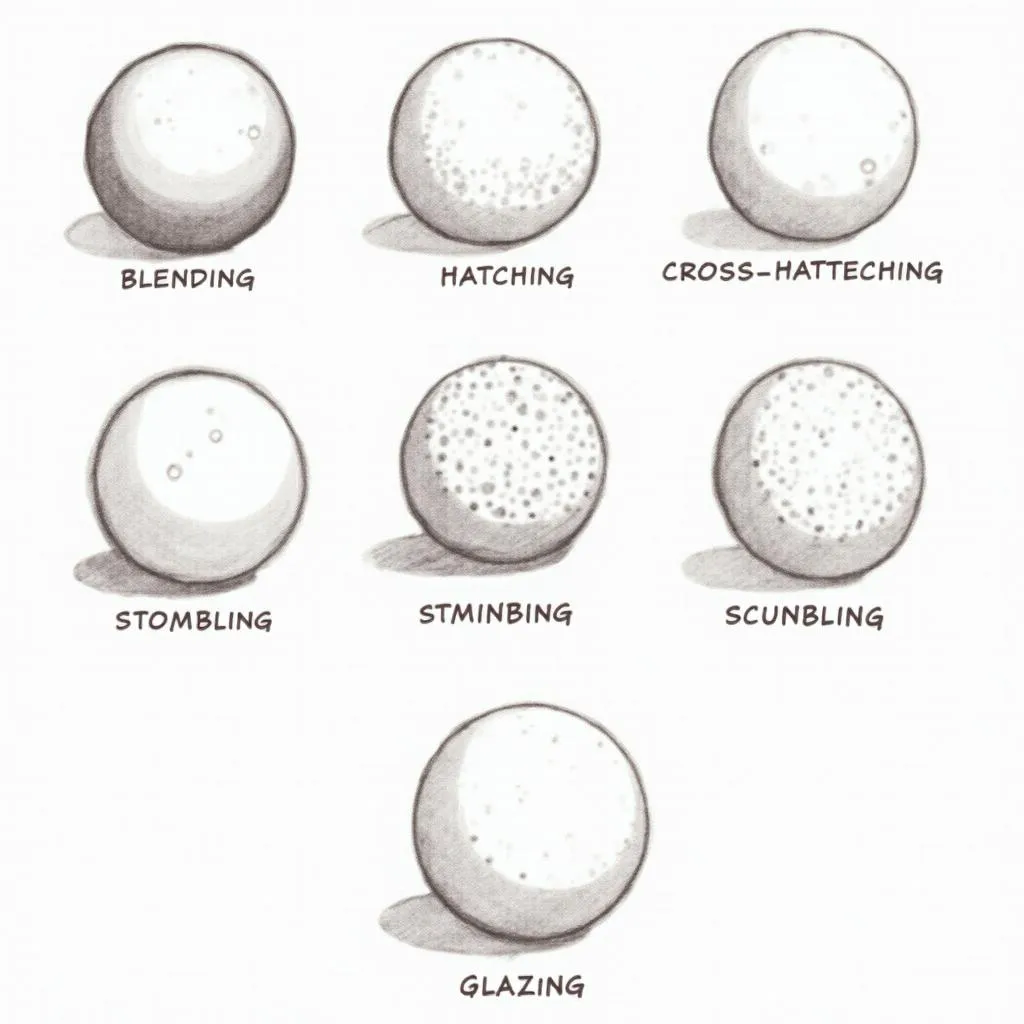 Examples of Different Shading Techniques
Examples of Different Shading Techniques
Tips for Effective Shading
Here are some valuable tips to elevate your shading skills:
- Observe Light and Shadow: Pay close attention to how light interacts with real-life objects. Identify the direction of the light source, the cast shadows, and the subtle variations in value.
- Practice with Value Scales: Create value scales for your chosen colors to familiarize yourself with the range of values available. This will help you create smooth transitions and accurate shading.
- Layer Your Colors: Building up color gradually in thin layers allows for greater control and subtlety. Avoid applying too much color at once, as this can lead to muddy results.
- Experiment with Different Techniques: Don’t be afraid to try different shading techniques and combine them to achieve unique effects.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Like any skill, mastering shading takes time and practice. The more you experiment and refine your technique, the better you’ll become.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of shading with colors is an ongoing journey of exploration and refinement. By understanding the principles of color theory, experimenting with different techniques, and practicing consistently, you can unlock a world of creative possibilities and bring your artistic visions to life with depth, dimension, and captivating realism.
FAQs
Q: What are the best colors for shading?
A: There are no “best” colors for shading, as the ideal choice depends on your chosen color palette and the overall mood you want to create. However, neutral colors like grays and browns are often used for shading as they don’t alter the hue of the base color significantly.
Q: How do I shade with colored pencils?
A: Shading with colored pencils involves layering and blending different pressures and colors to create smooth transitions. Start with light layers and gradually increase pressure to build up value.
Q: Can I use white to shade?
A: While white can be used to lighten areas, it’s generally not recommended for shading as it can create a chalky appearance. Instead, use lighter values of your chosen color to create highlights.
Q: What is the difference between shading and shadowing?
A: Shading refers to the overall process of adding value to create the illusion of form and depth. Shadowing, on the other hand, specifically refers to the dark areas where light is blocked.
Q: How can I improve my shading skills?
A: The key to improving your shading skills is practice. Experiment with different techniques, observe light and shadow in real life, and study the works of master artists for inspiration.
Need Help With Your Next Project?
If you need expert guidance on color selection or help bringing your design vision to life, don’t hesitate to reach out. Contact us at:
Phone: 0373298888
Email: [email protected]
Address: 86 Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội
Our team of color specialists and design professionals is available 24/7 to assist you with all your painting and design needs.