Color is a fascinating aspect of our world, influencing our perceptions and emotions. But have you ever stopped to think about the nature of color itself? Is color a chemical or physical property? The answer is more nuanced than you might think. Let’s dive into the captivating world of color and explore this intriguing question. After reading this, you’ll have a clearer understanding of what contributes to the vibrant hues we see around us. You might also want to learn more about specific colors, for instance, is blue color a physical or chemical property?
Understanding Physical and Chemical Properties
To determine whether color is a chemical or physical property, we first need to define these terms. A physical property is a characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the substance’s composition. Examples include density, melting point, and boiling point. A chemical property, on the other hand, describes a substance’s potential to undergo a chemical change or reaction, altering its composition. Examples include flammability and reactivity.
Now, let’s apply this knowledge to color.
 Color Spectrum Through a Prism
Color Spectrum Through a Prism
The Role of Light and Wavelength in Color Perception
Color, as we perceive it, is the result of the interaction between light and matter. When light strikes an object, certain wavelengths are absorbed, while others are reflected. The reflected wavelengths are what we see as color. This interaction doesn’t change the chemical composition of the object. Therefore, the color we observe is primarily related to a physical interaction, making it a physical property. For example, the vibrant green of a leaf results from the reflection of green wavelengths, while the other wavelengths are absorbed. The leaf remains chemically unchanged. You can learn more about specific color properties by exploring resources such as “is blue color a physical property”.
How Does Light Affect the Colors We See?
Different materials absorb and reflect light differently. This difference in interaction leads to the diversity of colors we see. The specific wavelengths absorbed and reflected are determined by the arrangement of electrons within the material’s atoms. When electrons absorb light energy, they jump to a higher energy level. When they return to their original state, they emit light of a specific wavelength, resulting in the color we see.
Chemical Changes and Color Change
While the initial color we observe is a physical property, a change in color can often indicate a chemical change. For instance, rusting iron changes from metallic gray to reddish-brown due to a chemical reaction with oxygen. In this case, the color change signals a change in the chemical composition of the iron, forming iron oxide. This concept is further explored in articles like “is color a physical or chemical change.” You can also explore “what color is obsidian” for another example of color related to chemical composition.
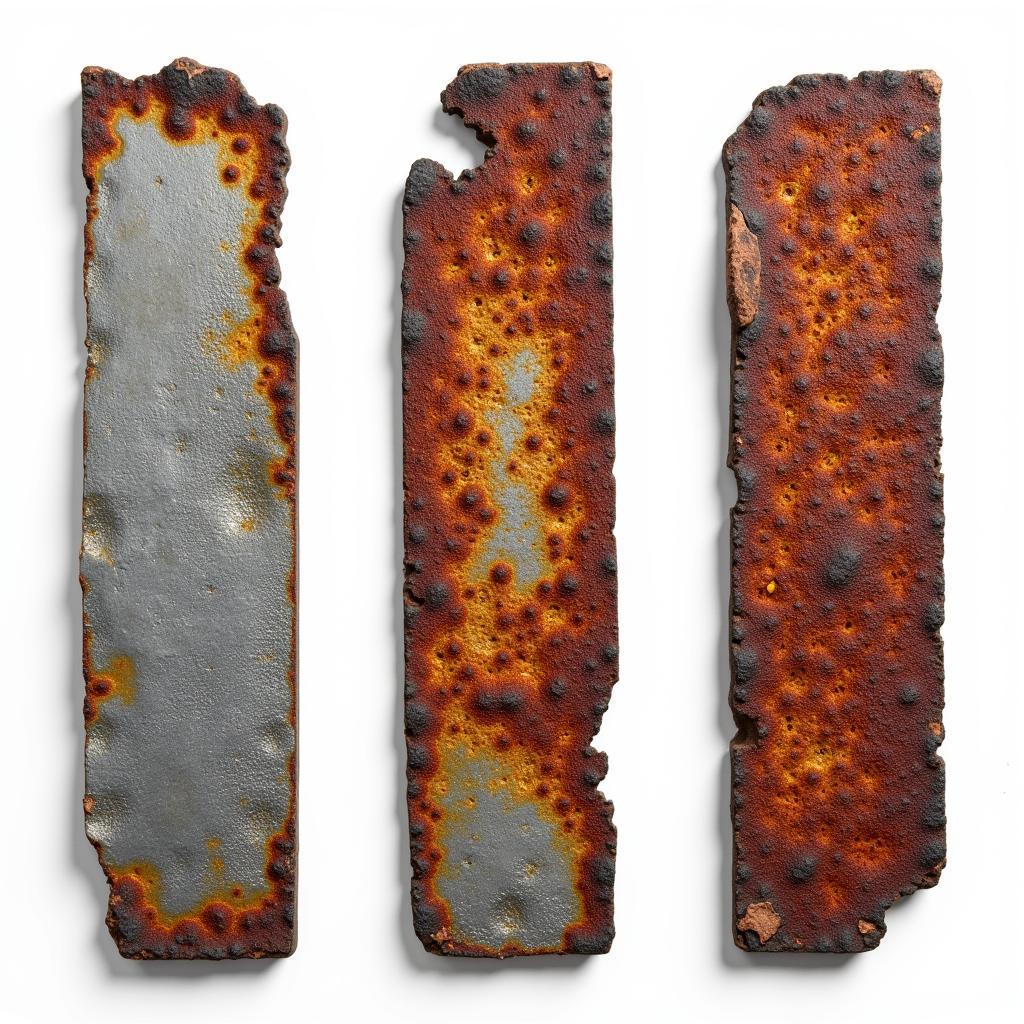 Rusting Iron Demonstrating a Chemical Change
Rusting Iron Demonstrating a Chemical Change
Color as an Indicator in Chemical Reactions
The color change observed during chemical reactions can be a valuable tool for chemists. It can be used to identify substances, monitor reaction progress, or determine the endpoint of a titration. The intensity of the color can also provide information about the concentration of a particular substance.
Examples of Color Change in Chemical Reactions
Numerous chemical reactions involve noticeable color changes. For example, the reaction between iodine and starch produces a deep blue-black color. This characteristic is often used as an indicator in titrations involving iodine. Another example is the color change observed during the burning of magnesium, where the bright white light emitted indicates a chemical reaction taking place.
Conclusion
So, is color a chemical or physical property? Primarily, the color we perceive is a physical property related to the interaction of light with matter. However, a change in color can often signal a chemical change. Understanding the interplay between light, matter, and chemical reactions gives us a deeper appreciation for the colorful world around us. Want to delve deeper into specific colors? Check out “is blue color a chemical or physical property”.
FAQ
- What is the difference between a physical and chemical property?
- How does light determine the color we see?
- Why does a change in color sometimes indicate a chemical reaction?
- Can color be used to identify substances?
- What are some examples of chemical reactions that involve color change?
- What is the relationship between wavelength and color?
- How does the arrangement of electrons affect color?
Need help with your next painting project? We at Color Box Hanoi can help you choose the perfect color palette for your space. Contact us at Phone: 0373298888, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 86 Cầu Giấy, Hanoi. We have a 24/7 customer service team.