Is color physical or chemical? This question often sparks curiosity, especially when we consider the vibrant hues surrounding us. Understanding the nature of color involves delving into the fascinating interplay of light, matter, and perception. is color a physical or chemical
Decoding the Nature of Color: Physical or Chemical?
Color, as we perceive it, is primarily a physical phenomenon rooted in the interaction of light and matter. However, the chemical composition of objects plays a crucial role in determining which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected, ultimately influencing the color we see.
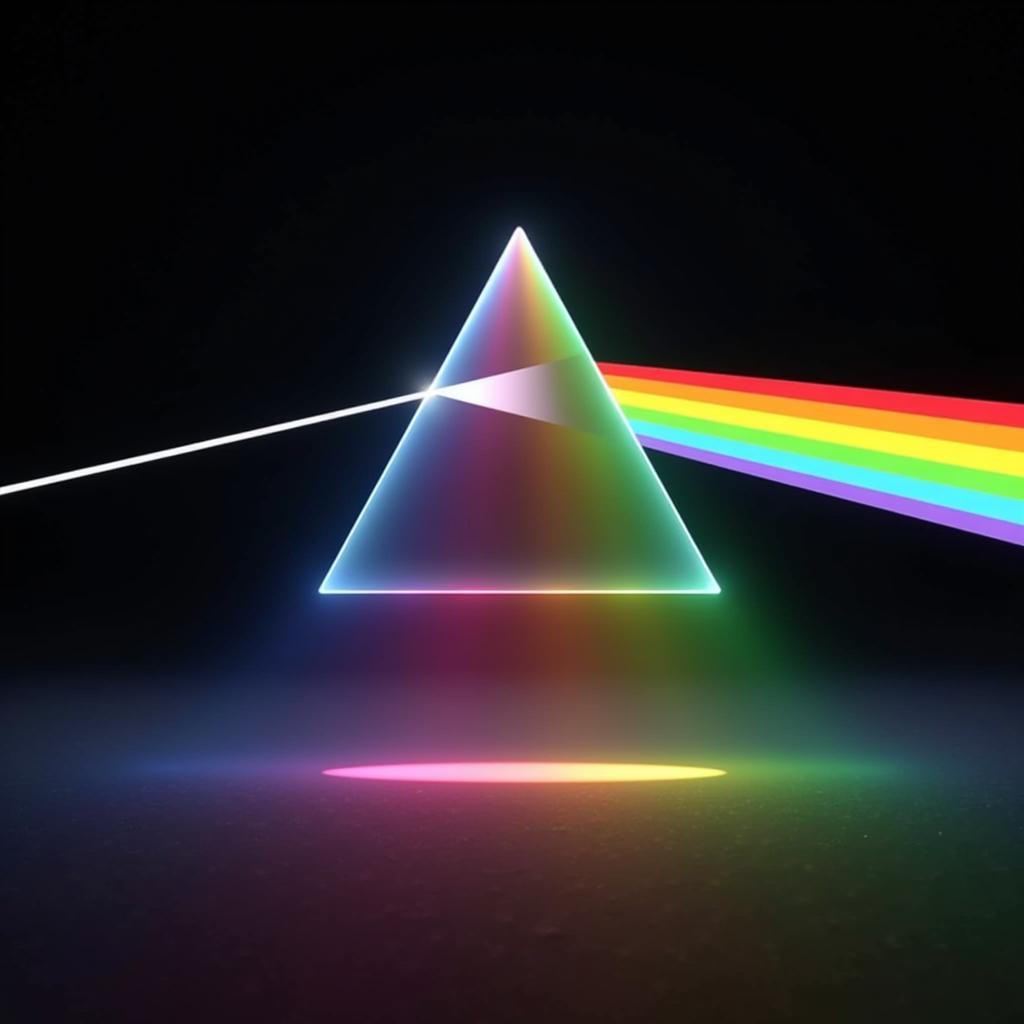 Light Wavelength Interaction and Color Perception
Light Wavelength Interaction and Color Perception
Think of a ripe strawberry. Its vibrant red color isn’t inherent to the strawberry itself but rather a result of its chemical makeup. The pigments within the strawberry absorb most wavelengths of light except for those in the red spectrum, which are reflected back to our eyes. This selective absorption and reflection are governed by the chemical structure of the pigments.
However, the perception of color is also influenced by physical factors such as the lighting conditions. The same strawberry might appear darker red under dim lighting or even slightly purplish under certain types of artificial light. This variation demonstrates the physical aspect of color perception, highlighting how the light source affects the wavelengths reaching our eyes. is the color blue a physical or chemical property
The Role of Chemical Composition in Color
The chemical composition of a substance dictates its interaction with light. Different substances possess unique molecular structures that absorb and reflect light in distinct ways. This characteristic is crucial in determining the color of paints, dyes, and pigments.
For example, the blue pigment in your favorite paint contains specific chemical compounds that absorb red, orange, yellow, green, indigo, and violet light, reflecting primarily blue light. This selective absorption and reflection are a direct consequence of the chemical properties of the pigment.
“The intricate relationship between chemical structure and light absorption is at the heart of color science,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading color chemist. “Understanding this relationship allows us to create a vast spectrum of colors using different chemical formulations.”
Physical Properties and Color Perception
While chemical composition determines which wavelengths are absorbed and reflected, physical properties like surface texture and the angle of incidence of light also influence color perception.
A smooth surface reflects light more uniformly, resulting in a more intense color. In contrast, a rough surface scatters light in different directions, leading to a less vibrant or even a slightly different perceived color. The angle at which light strikes an object also affects the wavelengths reaching our eyes, further influencing the color we see. is color a physical or chemical property
Conclusion
So, is color physical or chemical? It’s a fascinating interplay of both. The chemical properties of a substance determine its interaction with light, dictating which wavelengths are absorbed and reflected. However, the perception of color is also influenced by physical factors like lighting conditions and surface texture. This intricate relationship between light, matter, and perception makes color a captivating subject of study. For any color-related inquiries, contact us at 0373298888, [email protected], or visit us at 86 Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội. Our 24/7 customer service team is ready to assist you.
FAQ
-
What determines the color of an object? The chemical composition and the way it interacts with light.
-
Why do objects appear different colors under different lighting? The light source affects the wavelengths reaching our eyes.
-
How do pigments create color? They selectively absorb and reflect specific wavelengths of light.
-
Does surface texture affect color perception? Yes, a rough surface scatters light, impacting perceived color.
-
Is color solely a chemical property? No, it’s an interplay of chemical and physical factors.
 Color Perception: Human Eye and Brain Interpretation
Color Perception: Human Eye and Brain Interpretation
is color changing milk a chemical or physical change
Is color changing milk a chemical or physical change? This is another question related to color and changes in matter. is color a chemical or physical property
“Remember,” adds Professor David Miller, a renowned physicist, “color as we experience it is a subjective perception based on the physical interaction of light and our visual system, which is inherently linked to the chemical makeup of the objects we observe.”
See our other articles about “is color a physical or chemical property” for more in-depth information. Contact us at 0373298888, [email protected], or visit us at 86 Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội for all your color needs. We have a 24/7 customer service team.

